 | Info
Sheets |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
 | Out-
side |
| | | | |
|
| | | | |
Result : Searchterm 'Arc' found in 6 terms [ ] and 60 definitions [ ] and 60 definitions [ ] ]
| previous 46 - 50 (of 66) nextResult Pages :  [1 2] [1 2]  [3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14] [3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14] |  | |  | Searchterm 'Arc' was also found in the following services: | | | | |
|  |  |
| |
|
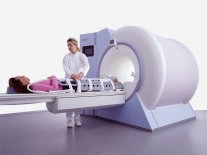
From Siemens Medical Systems;
while older navigator techniques take up to 40 minutes to create, the high performance of the MAGNETOM Sonata system enables 'complete examinations in less than 15 minutes'. It creates a new standard of diagnostic confidence and moves Cardiac MR from the rese arch setting into routine clinical practice.
Device Information and Specification CLINICAL APPLICATION Whole body Body, head, spine, knee, neck, TMJ, extremity, head, breast, shoulder, others GRE, IR, FIR, STIR, TrueIR/FISP, FSE, FLAIR, MT, SS-FSE, MT-SE, MTC, MSE, EPI, 3D DESS//CISS/PSIF, GMR IMAGING MODES Single, multislice, volume study, multi angle, multi oblique178 images/sec at 256 x 256 at 100% FOV1024 x 1024 full screen display 4050kg, 5500kg in operation POWER REQUIREMENTS 380/400/420/440/480 V Passive, act.; 1st order std./2nd opt. | |  | | | | | | | | |
|  |  | Searchterm 'Arc' was also found in the following services: | | | | |
|  |  |
| |
|
•
In the 1930's, Isidor Isaac Rabi (Columbia University) succeeded in detecting and measuring single states of rotation of atoms and molecules, and in determining the mechanical and magnetic moments of the nuclei.
•
Felix Bloch (Stanford University) and Edward Purcell (Harvard University) developed instruments, which could measure the magnetic resonance in bulk material such as liquids and solids. (Both honored with the Nobel Prize for Physics in 1952.) [The birth of the NMR spectroscopy]
•
In the early 70's, Raymond Damadian (State University of New York) demonstrated with his NMR device, that there are different T1 relaxation times between normal and abnormal tissues of the same type, as well as between different types of normal tissues.
•
In 1973, Paul Lauterbur (State University of New York) described a new imaging technique that he termed Zeugmatography. By utilizing gradients in the magnetic field, this technique was able to produce a two-dimensional image (back-projection). (Through analysis of the characteristics of the emitted radio waves, their origin could be determined.) Peter Mansfield further developed the utilization of gradients in the magnetic field and the mathematically analysis of these signals for a more useful imaging technique. (Paul C Lauterbur and Peter Mansfield were awarded with the 2003 Nobel Prize in Medicine.)
•
1977/78: First images could be presented.
A cross section through a finger by Peter Mansfield and Andrew A. Maudsley.
Peter Mansfield also could present the first image through the abdomen.
•
In 1977, Raymond Damadian completed (after 7 years) the first MR scanner (Indomitable). In 1978, he founded the FONAR Corporation, which manufactured the first commercial MRI scanner in 1980. Fonar went public in 1981.
•
1981: Schering submitted a patent application for Gd-DTPA dimeglumine.
•
1982: The first 'magnetization-transfer' imaging by Robert N. Muller.
•
In 1983, Toshiba obtained approval from the Ministry of Health and Welfare in Japan for the first commercial MRI system.
•
1986: Jürgen Hennig, A. Nauerth, and Hartmut Friedburg (University of Freiburg) introduced RARE (rapid acquisition with relaxation enhancement) imaging. Axel Haase, Jens Frahm, Dieter Matthaei, Wolfgang Haenicke, and Dietmar K. Merboldt (Max-Planck-Institute, Göttingen) developed the FLASH ( fast low angle shot) sequence.
•
1988: Schering's MAGNEVIST gets its first approval by the FDA.
•
In 1991, fMRI was developed independently by the University of Minnesota's Center for Magnetic Resonance Rese arch (CMRR) and Massachusetts General Hospital's (MGH) MR Center.
•
From 1992 to 1997 Fonar was paid for the infringement of it's patents from 'nearly every one of its competitors in the MRI industry including giant multi-nationals as Toshiba, Siemens, Shimadzu, Philips and GE'.
| | | |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'MRI History' (6).
| | |
• View the NEWS results for 'MRI History' (1).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | | Basics:
|
|
News & More:
| |
| |
|  | |  |  |  |
| |
|
The subacute risks and side effects of magnetic and RF fields (for patients and staff) have been intensively examined for a long time, but there have been no long-term studies following persons who have been exposed to the static magnetic fields used in MRI. However, no permanent hazardous effects of a static magnetic field exposure upon human beings have yet been demonstrated.
Temporary possible side effects of high magnetic and RF fields:
•
Varying magnetic fields can induce so-called magnetic phosphenes that occur when an individual is subject to rapid changes of 2-5 T/s, which can produce a flashing sensation in the eyes. This temporary side effect does not seem to damage the eyes. Static field strengths used for clinical MRI examinations vary between 0.2 and 3.0 tesla;; field changes during the MRI scan vary in the dimension of mT/s. Experimental imaging units can use higher field strengths of up to 14.0 T, which are not approved for human use.
•
The Radio frequency pulses mainly produce heat, which is absorbed by the body tissue. If the power of the RF radiation is very high, the patient may be heated too much. To avoid this heating, the limit of RF exposure in MRI is up to the maximum specific absorption rate (SAR) of 4 W/kg whole body weight (can be different from country to country). For MRI safety reasons, the MRI machine starts no sequence, if the SAR limit is exceeded.
•
Very high static magnetic fields are needed to reduce the conductivity of nerves perceptibly. Augmentation of T waves is observed at fields used in standard imaging but this side effect in MRI is completely reversible upon removal from the magnet. Cardiac arrhythmia threshold is typically set to 7-10 tesla. The magnetohydrodynamic effect, which results from a voltage occurring across a vessel in a magnetic field and percolated by a saline solution such as blood, is irrelevant at the field strengths used.
The results of some animal and cellular studies suggest the possibility that electromagnetic fields may act as co-c arcinogens or tumor promoters, but the data are inconclusive.
Up to 45 tesla, no important effects on enzyme systems have been observed. Neither changes in enzyme kinetics, nor orientation changes in macromolecules have been conclusively demonstrated.
There are some publications associating an increase in the incidence of leukemia with the location of buildings close to high-current power lines with extremely low-frequency (ELF) electromagnetic radiation of 50-60 Hz, and industrial exposure to electric and magnetic fields but a transposition of such effects to MRI or MRS seems unlikely.
Under consideration of the MRI safety guidelines, real dangers or risks of an exposure with common MRI field strengths up to 3 tesla as well as the RF exposure during the MRI scan, are not to be expected.
For more MRI safety information see also Nerve Conductivity,
Contraindications, Pregnancy
and Specific Absorption Rate.
See also the related poll result: ' In 2010 your scanner will probably work with a field strength of' | |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'MRI Risks' (9).
| | |
• View the NEWS results for 'MRI Risks' (3).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | | Basics:
|
|
News & More:
| |
| |
|  |  | Searchterm 'Arc' was also found in the following services: | | | | |
|  |  |
| |
|
The definition of a scan is to form an image or an electronic representation. The MRI scan uses magnetic resonance principles to produce extremely detailed pictures of the body tissue without the need for X-ray exposure or other damaging forms of radiation.
MRI scans show structures of the different tissues in the body. The tissue that has the least hydrogen atoms (e.g., bones) appears dark, while the tissue with many hydrogen atoms (e.g., fat) looks bright. The MRI pictures of the brain show details and abnormal structures ( brain MRI), for example, tumors, multiple sclerosis lesions, bleedings, or brain tissue that has suffered lack of oxygen after a stroke.
A cardiac MRI scan demonstrates the heart as well as blood vessels ( cardiovascular imaging) and is used to detect heart defects with e.g., changes in the thickness and inf arctions of the muscles around the heart. With MRI scans, nearly all kind of body parts can be tested, for example the joints like knee and shoulder, lumbar, thoracic and cervical spine, the pelvis including fetal MRI, and the soft parts of the body such as the liver, kidneys, and spleen.
The MRI procedure includes three to nine imaging sequences and may take up to one hour. See also Lumbar Spine MRI, MRI Safety and Open MRI. | | | | | | | | | | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'MRI Scan' (31).
| | |
• View the NEWS results for 'MRI Scan' (95).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | Basics:
|
|
News & More:
|  |
A Knee MRI in Half the Time? It's Possible
Thursday, 8 April 2021 by www.diagnosticimaging.com |  |  |
Michigan radiologist warns about 'incidental findings' in full body MRI scans
Wednesday, 4 October 2023 by www.wilx.com |  |  |
ACCELERATING MRI SCANS WITH ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE
Friday, 28 August 2020 by www.analyticsinsight.net |  |  |
Radiographer's Lego Open MRI Product Idea Reaches New Milestone
Monday, 11 November 2019 by www.itnonline.com |  |  |
Why we need erasable MRI scans
Wednesday, 25 April 2018 by phys.org |  |  |
MRI as accurate as CT for Crohn's disease detection, management
Tuesday, 6 June 2017 by www.healthimaging.com |  |  |
MRI scans predict patients' ability to fight the spread of cancer
Tuesday, 12 December 2017 by eurekalert.org |  |  |
Audio/Video System helps patients relax during MRI scans
Monday, 8 December 2014 by news.thomasnet.com |  |  |
MRI scans could be a 'game-changer' in prostate cancer testing
Tuesday, 5 August 2014 by www.abc.net.au |  |  |
7-Tesla MRI scanner allows even more accurate diagnosis of breast cancer
Thursday, 6 March 2014 by www.healthcanal.com |
|
| |
|  |  | Searchterm 'Arc' was also found in the following services: | | | | |
|  |  |
| |
|
(MRS / MRSI - Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopic Imaging) A method using the NMR phenomenon to identify the chemical state of various elements without destroying the sample. MRS therefore provides information about the chemical composition of the tissues and the changes in chemical composition, which may occur with disease processes.
Although MRS is primarily employed as a rese arch tool and has yet to achieve widespread acceptance in routine clinical practice, there is a growing realization that a noninvasive technique, which monitors disease biochemistry can provide important new information for the clinician.
The underlying principle of MRS is that atomic nuclei are surrounded by a cloud of electrons, which very slightly shield the nucleus from any external magnetic field. As the structure of the electron cloud is specific to an individual molecule or compound, then the magnitude of this screening effect is also a characteristic of the chemical environment of individual nuclei.
In view of the fact that the resonant frequency is proportional to the magnetic field that it experiences, it follows that the resonant frequency will be determined not only by the external applied field, but also by the small field shift generated by the electron cloud.
This shift in frequency is called the chemical shift (see also Chemical Shift). It should be noted that chemical shift is a very small effect, usually expressed in ppm of the main frequency. In order to resolve the different chemical species, it is therefore necessary to achieve very high levels of homogeneity of the main magnetic field B0.
Spectra from humans usually require shimming the magnet to approximately one part in 100. High resolution spectra of liquid samples demand a homogeneity of about one part in 1000.
In addition to the effects of factors such as relaxation times that can affect the NMR signal, as seen in magnetic resonance imaging, effects such as J-modulation or the transfer of magnetization after selective excitation of particular spectral lines can affect the relative strengths of spectral lines.
In the context of human MRS, two nuclei are of particular interest - H-1 and P-31. (PMRS - Proton Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy) PMRS is mainly employed in studies of the brain where prominent peaks arise from NAA, choline containing compounds, creatine and creatine phosphate, myo-inositol and, if present, lactate; phosphorus 31 MR spectroscopy detects compounds involved in energy metabolism (creatine phosphate, adenosine triphosphate and inorganic phosphate) and certain compounds related to membrane synthesis and degradation. The frequencies of certain lines may also be affected by factors such as the local pH. It is also possible to determine intracellular pH because the inorganic phosphate peak position is pH sensitive.
If the field is uniform over the volume of the sample, "similar" nuclei will contribute a particular frequency component to the detected response signal irrespective of their individual positions in the sample. Since nuclei of different elements resonate at different frequencies, each element in the sample contributes a different frequency component. A chemical analysis can then be conducted by analyzing the MR response signal into its frequency components.
See also Spectroscopy. | |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy' (8).
| | |
• View the NEWS results for 'Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy' (3).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | News & More:
|
|
| |
|  | |  |  |
|  | | |
|
| |
 | Look
Ups |
| |