 | Info
Sheets |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
 | Out-
side |
| | | | |
|
| | | | |
Result : Searchterm 'T2 Weighted' found in 2 terms [ ] and 44 definitions [ ] and 44 definitions [ ] ]
| 1 - 5 (of 46) nextResult Pages :  [1] [1]  [2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10] [2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10] |  | |  | Searchterm 'T2 Weighted' was also found in the following services: | | | | |
|  |  |
| T2 Weighted |  |
| |
|
Often used to indicate an image where most of the contrast between tissues or tissue states is due to differences in tissue T2 created typically by using longer TE and TR times.
This term may be misleading in that the potentially important effects of tissue density differences and the range of tissue T2 values are often ignored.
Choosing the machine parameters such that TR greater than T1 (typically greater than 2 000 ms) and TE less than T2 (typically greater than 100 ms) and noting that (1-exp(-TR/T1) = 1 for TR/T1 much greater than 1, will reduce Eq. 1 to the expression
Mxy = Mxy0exp(-TE/T2)
which is dependent on T2 only, hence the term T2 weighting.
Therefore T2 weighted image contrast state is approached by imaging with a TR long compared to tissue T1 (to reduce T1 contribution to image contrast) and a TE between the longest and shortest tissue T2s of interest. A TR greater than 3 times the longest T1 is required for the T1 effect to be less than 5%. Due to the wide range of T1 and T2 and tissue density values that can be found in the body, an image that is T2 weighted for some tissues may not be so for others.
See also T2 Time.
Lesions with short T2 are (dark in T2 weighted sequences): acute haemorrhage (deoxyHb)
haemosiderin
physiologic iron (basal ganglia, etc.)
mucinous lesions. | | | |  | | | | • Share the entry 'T2 Weighted':    | | | | | | | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | | Basics:
|
|
News & More:
| |
| |
|  | |  |  |  |
| |
|
T2 weighted imaging relies upon local dephasing of spins following the application of the transverse energy pulse. The contrast of a T2 weighted image is predominantly dependent on T2 and the T2 dependence will be increased by using a long echo time.
Fat has a shorter T2 time than water and relaxes or decays more readily than water. Since the amount of transverse magnetization in fat is small, fat generates very little signal on a strong T2 weighted contrast image and appears intermediate to dark. The T2 weighting is stronger with a longer TE. Water has a very high T2 constant, therefore has very high T2 signal and thus appears bright on a T2 contrast image. Cerebral white matter (fat containing) is less intense than grey matter. Flowing blood ( flow effects) and haematomas ( haemoglobin, haemosiderin) have a variable signal intensity on MR images.
Images created with TR's and TE's to enhance T2 contrast are referred to as T2 weighted images.
Both T1 and T2 weighted images are acquired for most medical MRI examinations. | | | |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'T2 Weighted Image' (5).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | Basics:
|
|
News & More:
| |
| |
|  | |  |  |  |
| |
|
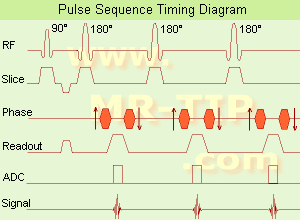
(FSE) In the pulse sequence timing diagram, a fast spin echo sequence with an echo train length of 3 is illustrated.
This sequence is characterized by a series of rapidly applied 180° rephasing pulses and multiple echoes, changing the phase encoding gradient for each echo.
The echo time TE may vary from echo to echo in the echo train. The echoes in the center of the K-space (in the case of linear k-space acquisition) mainly produce the type of image contrast, whereas the periphery of K-space determines the spatial resolution. For example, in the middle of K-space the late echoes of T2 weighted images are encoded. T1 or PD contrast is produced from the early echoes.
The benefit of this technique is that the scan duration with, e.g. a turbo spin echo turbo factor / echo train length of 9, is one ninth of the time. In T1 weighted and proton density weighted sequences, there is a limit to how large the ETL can be (e.g. a usual ETL for T1 weighted images is between 3 and 7). The use of large echo train lengths with short TE results in blurring and loss of contrast. For this reason, T2 weighted imaging profits most from this technique.
In T2 weighted FSE images, both water and fat are hyperintense. This is because the succession of 180° RF pulses reduces the spin spin interactions in fat and increases its T2 decay time. Fast spin echo (FSE) sequences have replaced conventional T2 weighted spin echo sequences for most clinical applications. Fast spin echo allows reduced acquisition times and enables T2 weighted breath hold imaging, e.g. for applications in the upper abdomen.
In case of the acquisition of 2 echoes this type of a sequence is named double fast spin echo / dual echo sequence, the first echo is usually density and the second echo is T2 weighted image. Fast spin echo images are more T2 weighted, which makes it difficult to obtain true proton density weighted images. For dual echo imaging with density weighting, the TR should be kept between 2000 - 2400 msec with a short ETL (e.g., 4).
Other terms for this technique are:
Turbo Spin Echo
Rapid Imaging Spin Echo,
Rapid Spin Echo,
Rapid Acquisition Spin Echo,
Rapid Acquisition with Refocused Echoes
| | | |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'Fast Spin Echo' (31).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | Basics:
|
|
News & More:
| |
| |
|  |  | Searchterm 'T2 Weighted' was also found in the following services: | | | | |
|  |  |
| |
|
General MRI of the abdomen can consist of T1 or T2 weighted spin echo, fast spin echo ( FSE, TSE) or gradient echo sequences with fat suppression and contrast enhanced MRI techniques. The examined organs include liver, pancreas, spleen, kidneys, adrenals as well as parts of the stomach and intestine (see also gastrointestinal imaging). Respiratory compensation and breath hold imaging is mandatory for a good image quality.
T1 weighted sequences are more sensitive for lesion detection than T2 weighted sequences at 0.5 T, while higher field strengths (greater than 1.0 T), T2 weighted and spoiled gradient echo sequences are used for focal lesion detection.
Gradient echo in phase T1 breath hold can be performed as a dynamic series with the ability to visualize the blood distribution. Phases of contrast enhancement include the capillary or arterial dominant phase for demonstrating hypervascular lesions, in liver imaging the portal venous phase demonstrates the maximum difference between the liver and hypovascular lesions, while the equilibrium phase demonstrates interstitial disbursement for edematous and malignant tissues.
Out of phase gradient echo imaging for the abdomen is a lipid-type tissue sensitive sequence and is useful for the visualization of focal hepatic lesions, fatty liver (see also Dixon), hemochromatosis, adrenal lesions and renal masses.
The standards for abdominal MRI vary according to clinical sites based on sequence availability and MRI equipment.
Specific abdominal imaging coils and liver-specific contrast agents targeted to the healthy liver tissue improve the detection and localization of lesions.
See also Hepatobiliary Contrast Agents, Reticuloendothelial Contrast Agents, and Oral Contrast Agents.
For Ultrasound Imaging (USI) see Abdominal Ultrasound at Medical-Ultrasound-Imaging.com. | | | |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'Abdominal Imaging' (11).
| | |
• View the NEWS results for 'Abdominal Imaging' (3).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | Basics:
|
|
News & More:
|  |
Assessment of Female Pelvic Pathologies: A Cross-Sectional Study Among Patients Undergoing Magnetic Resonance Imaging for Pelvic Assessment at the Maternity and Children Hospital, Qassim Region, Saudi Arabia
Saturday, 7 October 2023 by www.cureus.com |  |  |
Higher Visceral, Subcutaneous Fat Levels Predict Brain Volume Loss in Midlife
Wednesday, 4 October 2023 by www.neurologyadvisor.com |  |  |
Deep Learning Helps Provide Accurate Kidney Volume Measurements
Tuesday, 27 September 2022 by www.rsna.org |  |  |
CT, MRI for pediatric pancreatitis interobserver agreement with INSPPIRE
Friday, 11 March 2022 by www.eurekalert.org |  |  |
Clinical trial: Using MRI for prostate cancer diagnosis equals or beats current standard
Thursday, 4 February 2021 by www.eurekalert.org |  |  |
Computer-aided detection and diagnosis for prostate cancer based on mono and multi-parametric MRI: A review - Abstract
Tuesday, 28 April 2015 by urotoday.com |  |  |
Nottingham scientists exploit MRI technology to assist in the treatment of IBS
Thursday, 9 January 2014 by www.news-medical.net |  |  |
New MR sequence helps radiologists more accurately evaluate abnormalities of the uterus and ovaries
Thursday, 23 April 2009 by www.eurekalert.org |  |  |
MRI identifies 'hidden' fat that puts adolescents at risk for disease
Tuesday, 27 February 2007 by www.eurekalert.org |
|
| |
|  | |  |  |  |
| |
|
Contrast is the relative difference of signal intensities in two adjacent regions of an image.
Due to the T1 and T2 relaxation properties in magnetic resonance imaging, differentiation between various tissues in the body is possible. Tissue contrast is affected by not only the T1 and T2 values of specific tissues, but also the differences in the magnetic field strength, temperature changes, and many other factors. Good tissue contrast relies on optimal selection of appropriate pulse sequences ( spin echo, inversion recovery, gradient echo, turbo sequences and slice profile).
Important pulse sequence parameters are TR ( repetition time), TE (time to echo or echo time), TI (time for inversion or inversion time) and flip angle. They are associated with such parameters as proton density and T1 or T2 relaxation times. The values of these parameters are influenced differently by different tissues and by healthy and diseased sections of the same tissue.
For the T1 weighting it is important to select a correct TR or TI. T2 weighted images depend on a correct choice of the TE. Tissues vary in their T1 and T2 times, which are manipulated in MRI by selection of TR, TI, and TE, respectively. Flip angles mainly affect the strength of the signal measured, but also affect the TR/TI/TE parameters.
Conditions necessary to produce different weighted images:
T1 Weighted Image: TR value equal or less than the tissue specific T1 time - TE value less than the tissue specific T2 time.
T2 Weighted Image: TR value much greater than the tissue specific T1 time - TE value greater or equal than the tissue specific T2 time.
Proton Density Weighted Image: TR value much greater than the tissue specific T1 time - TE value less than the tissue specific T2 time.
See also Image Contrast Characteristics, Contrast Reversal, Contrast Resolution, and Contrast to Noise Ratio. | | | |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'Contrast' (373).
| | |
• View the NEWS results for 'Contrast' (77).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | Basics:
|
|
News & More:
| |
| |
|  | |  |  |
|  | | |
|
| |
 | Look
Ups |
| |