(EPI)
Echo planar imaging is one of the early
magnetic resonance imaging sequences (also known as Intascan), used in applications like
diffusion, perfusion, and
functional magnetic resonance imaging. Other
sequences acquire one
k-space line at each
phase encoding step. When the
echo planar imaging acquisition strategy is used, the complete image is formed from a single data sample (all
k-space lines are measured in one
repetition time) of a
gradient echo or
spin echo sequence (see
single shot technique) with an
acquisition time of about 20 to 100 ms.
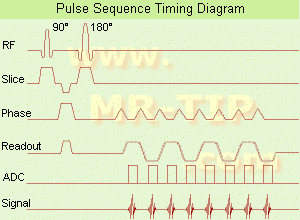
The
pulse sequence timing diagram illustrates an
echo planar
imaging sequence from
spin echo type with eight
echo train pulses. (See also
Pulse Sequence Timing Diagram, for a description of the components.)
In case of a
gradient echo based EPI sequence the initial part is very similar to a standard
gradient echo sequence. By periodically fast reversing the readout or
frequency encoding gradient, a train of echoes is generated.
EPI requires higher performance from the
MRI scanner like much larger
gradient amplitudes. The
scan time is dependent on the
spatial resolution required, the strength of the applied
gradient fields and the time the machine needs to
ramp the gradients.
In EPI, there is
water fat shift in the
phase encoding direction due to
phase accumulations. To minimize
water fat shift (WFS) in the
phase direction
fat suppression and a wide
bandwidth (BW) are selected. On a typical EPI sequence, there is virtually no time at all for the
flat top of the
gradient waveform. The problem is solved by "ramp sampling" through most of the rise and fall time to improve
image resolution.
The benefits of the fast imaging time are not without cost. EPI is relatively demanding on the scanner
hardware, in particular on
gradient strengths,
gradient switching times, and
receiver bandwidth. In addition, EPI is extremely sensitive to image artifacts and distortions.