 | Info
Sheets |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
 | Out-
side |
| | | | |
|
| | | | |
Result : Searchterm 'high field' found in 1 term [ ] and 35 definitions [ ] and 35 definitions [ ] ]
| previous 31 - 35 (of 36) nextResult Pages :  [1] [1]  [2 3 4 5 6 7 8] [2 3 4 5 6 7 8] |  | |  | Searchterm 'high field' was also found in the following services: | | | | |
|  |  |
| |
|
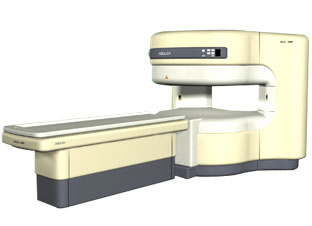
From ISOL Technology
'RELAX is open type MRI system created by making up for the weakness of existing conventional MR systems and applying the strength and the application of the middle to high field MR without uncompromising the image quality.
RELAX offers you a premium mix of form, performance and functionality that are patient and user
friendly beyond comparison.
- New breed of MRI pursuing
- patients comfort'
Device Information and Specification CLINICAL APPLICATION Whole body lower than 2.4 m from the iso-center | |  | | | |
|  | |  |  |  |
| |
|
Quick Overview
DESCRIPTION
Localized inhomogeneous brightness
HELP
Check the correct positioning, call the service
Uneven intensity or brightness may occasionally be noted on high field MRI e.g. of the brain. There are various causes of localized inhomogeneous brightness across the MRI images such as improper tuning of the RF transceiver, unbalanced deposition of the RF energy due to incorrect geometry and localized attenuation due to positioning or anatomical variants.

Image Guidance
Tuning of the RF transceiver, a homogeneity correction filter and better positioning of the scanned object and/or coil in the scanner. | |  | | | |
|  | |  |  |  |
| |
|
(SAR) The Specific Absorption Rate is defined as the RF power absorbed per unit of mass of an object, and is measured in watts per kilogram (W/kg).
The SAR describes the potential for heating of the patient's tissue due to the application of the RF energy necessary to produce the MR signal. Inhomogeneity of the RF field leads to a local exposure where most of the absorbed energy is applied to one body region rather than the entire person, leading to the concept of a local SAR. Hot spots may occur in the exposed tissue, to avoid or at least minimize effects of such theoretical complications, the frequency and the power of the radio frequency irradiation should be kept at the lowest possible level. Averaging over the whole body leads to the global SAR.
It increases with field strength, radio frequency power and duty cycle, transmitter-coil type and body size. The doubling of the field strength from 1.5 Tesla (1.5T) to 3 Tesla ( 3T) leads to a quadrupling of SAR. In high and ultra high fields, some of the multiple echo, multiple-slice pulse sequences may create a higher SAR than recommended by the agencies. SAR can be reduced by lower flip angle and longer repetition times, which could potentially affect image contrast.
Normally no threatening increase in temperature could be shown. Even in high magnetic fields, the local temperature increases not more than 1°C. 2.1°C is the highest measured increase in skin temperature. Eddy currents may heat up implants and thus may cause local heating.
FDA SAR limits:
•
Whole body: 4W/kg/15-minute exposure averaged;
•
Head: 3W/kg/10-minute exposure averaged;
•
Head or torso: 8W/kg/5 minute exposure per gram of tissue;
•
Extremities: 12W/kg/5 minute exposure per gram of tissue.
IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission) SAR limits of some European countries:
All limits are averaged over 6 minutes.
•
Level 0 (normal operating mode): Whole body 2W/kg; Head 3.2W/kg; Head or Torso (local) 10W/kg;
Extremities (local) 20W/kg;
•
Level I (first level controlled operating mode): Whole body 4W/kg; Head 3.2W/kg; Head or Torso (local) 10W/kg; Extremities (local) 20W/kg;
•
Level II (second level controlled operating mode): All values are over Level I values.
(For more details: IEC 60601-2-33 (2002))
In most countries standard MRI systems are limited to a maximum SAR of 4 W/kg, so most scanning in level II is impossible.
For Level I, in addition to routine monitoring, particular caution must be exercised for patients who are sensitive to temperature increases or to RF energy.
For Japan different SAR limits are valid. | |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'Specific Absorption Rate' (8).
| | |
• View the NEWS results for 'Specific Absorption Rate' (1).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | | Basics:
|
|
News & More:
| |
| |
|  |  | Searchterm 'high field' was also found in the following services: | | | | |
|  |  |
| |
|
(T/R) Also called transceiver coil. An RF coil that acts as a transmitter (T) producing the B1 excitation field and as a receiver (R) of the MRI signal. Such a coil requires a T/R switching circuit to switch between the two modes. A body coil is typically a T/R coil, but smaller volume T/R coils (head/extremities) are often used at high field as a possibility of reducing RF power absorption (SAR). | | | |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'Transmit Receive Coil' (4).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | Basics:
|
|
| |
|  | |  |  |  |
| |
|
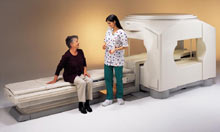
From Toshiba America Medical Systems Inc.;
the Ultra™ system was developed to help healthcare providers be more competitive by delivering greater patient comfort and a broad range of clinical capabilities, says Anita Bowler, product manager, MRI Business Unit, Toshiba America Medical Systems Inc With its unique, powerful gradient technology, the Ultra™ performs advanced clinical studies and consistently provides high-resolution images that are typically associated with high field MRI systems. At the same time, the Ultra™ offers a truly open feeling that makes patients more relaxed, especially those with claustrophobic tendencies.
Device Information and Specification CLINICAL APPLICATION Whole Body Quadrature, solenoid and multi-channel configurations SE, FE, IR, FastSE, FastIR, FastFLAIR, Fast STIR, FastFE, FASE, Hybrid EPI, Multi Shot EPI, Single shot EPI diffusion, True SSFP, SuperFASE; Angiography: 2D(gate/non-gate)/3D TOF, SORS-STC, Black Blood MRA POWER REQUIREMENTS 380/400/415/440/480 V COOLING SYSTEM TYPE Cryogenless | |  | | | |
|  | |  |  |
|  | |
|  | | |
|
| |
 | Look
Ups |
| |