 | Info
Sheets |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
 | Out-
side |
| | | | |
|
| | | | |
Result : Searchterm 'Solenoid Coil' found in 1 term [ ] and 0 definition [ ] and 0 definition [ ], (+ 13 Boolean[ ], (+ 13 Boolean[ ] results ] results
| previous 6 - 10 (of 14) nextResult Pages :  [1] [1]  [2 3] [2 3] |  | | |  |  |  |
| |
|
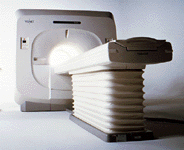
From Toshiba America Medical Systems Inc.;
VISARTâ„¢ series is a 1.5 Tesla superconducting MRI system that has been designed to meet the expanding role of MRI in today's clinical environment. The system utilizes innovative technologies such as digital RF, high speed actively shielded gradients and optimized RF coils, which support a wide range of MRI developments. The Visart, an early type of Toshiba Medical Systems Inc., can be retrofitted or upgraded to the Excelart configuration.
Device Information and Specification CLINICAL APPLICATION Whole body Quadrature, solenoid and multi-channel configurations SE, FE, IR, FastSE, FastIR, FastFLAIR, Fast STIR, FastFE, FASE, Hybrid EPI, Multi Shot EPI; Angiography: 2D(gate/non-gate)/3D TOF, SORS-STC IMAGING MODES Single, multislice, volume study POWER REQUIREMENTS 380/400/415/440/480 V COOLING SYSTEM TYPE Closed-loop water-cooled | |  | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | News & More:
|
|
| |
|  | |  |  |  |
| |
|
A coil is a large inductor with a considerable dimension and a defined wavelength, commonly used in configurations for MR imaging. The frequency of the radio frequency coil is defined by the Larmor relationship. The MRI image quality depends on the signal to noise ratio (SNR) of the acquired signal from the patient. Several MR imaging coils are necessary to handle the diversity of applications. Large coils have a large measurement field, but low signal intensity and vice versa (see also coil diameter). The closer the coil to the object, the stronger the signal - the smaller the volume, the higher the SNR. SNR is very important in obtaining clear images of the human body. The shape of the coil depends on the image sampling. The best available homogeneity can be reached by choice of the appropriate coil type and correct coil positioning. Orientation is critical to the sensitivity of the RF coil and therefore the coil should be perpendicular to the static magnetic field.
RF coils can be differentiated by there function into three general categories:
The RF signal is in the range of 10 to 100 MHz. During a typical set of clinical image measurements, the entire frequency spectrum of interest is of the order 10 kHz, which is an extremely narrow band, considering that the center frequency is about 100 MHz. This allows the use of single-frequency matching techniques for coils because their inherent bandwidth always exceeds the image bandwidth. The multi turn solenoid, bird cage coil, single turn solenoid, and saddle coil are typically operated as the transmitter and receiver of RF energy. The surface and phased array coils are typically operated as a receive only coil.
See also the related poll result: ' 3rd party coils are better than the original manufacturer coils' | | | |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'Radio Frequency Coil' (9).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | | Basics:
|
|
News & More:
| |
| |
|  | |  |  |  |
| |
|
A coil, or antenna, positioned within the imaging volume and connected to the receiver circuitry that is used to detect or receive the MR signal from the patient as the disturbed spins relax back into their equilibrium distribution. Also called receive-only coil.
Special-purpose coils are designed to optimize the SNR from a given region of the body. State-of-the-art coil systems include the use of four or more coils with four separate receivers. This method is often referred to as a phased array system.
Receiver coil types include also solenoid, planar, volume and quadrature coils.
The quality of the MR images depends on the SNR of the acquired signal
from the patient. SNR is of the utmost importance in obtaining clear images of the interior of the human body. | |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'Receiver Coil' (11).
| | | | |
|  | |  |  |  |
| |
|
A magnet is by definition an object with magnetic properties ( magnetism) that attracts iron and produces a magnetic field. It can be a permanent magnet or an electromagnet.
Permanent magnets do not rely upon outside influences to generate their field. In permanent magnets are the atoms and molecules ordered in long range. The specific electron configuration and the distance of the atoms is what lead to this long range ordering. The electrons exist in a lower energy state if they all have the same orientation. Magnetic domains can be likened to microscopic neighborhoods in which there is a strong reinforcing interaction between particles, resulting in a high degree of order. The greater the degree of ordering within and between domains, the greater the resulting field will be. Long range ordering is one of the hallmarks of a ferromagnetic material.
A current carrying conductor for example a piece of wire, produces a magnetic field that encircles the wire. An electromagnet, in its simplest form, is a wire that has been coiled into one or more loops. This coil is known as a solenoid. The more loops of wire and the greater the current, the stronger the field will be.
Superconducting magnets are a special type of electromagnets, often used in MRI machines with high field strength. | |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'Magnet' (669).
| | |
• View the NEWS results for 'Magnet' (315).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | | Basics:
|
|
News & More:
| |
| |
|  | |  |  |  |
| |
|
A surface coil is essentially a loop of conducting material, such as copper tubing. The in-bore solenoidal sending coil is used as the transmitter of RF energy. This type of receiver coil is placed directly on or over the region of interest for increased magnetic sensitivity. The loop may form various shapes and be bent slightly to conform to the imaged body part. Surface coils have a good SNR for tissues adjacent to the coil and because the signal decrease with the distance, an eligibility homogeneity correction will equalize this over the field of view. A rule of thumb for surface coils is that the sensitivity decreases appreciably beyond a distance equal to the diameter of the coil.
The positioning of the coil is an important determinant of performance. As only the region close to the surface coil will contribute to the signal, there is an improvement in the SNR for these regions, compared to the use of receiver coils that surround the appropriate part of the body. These coils are specifically designed for localized body regions, and provide improved signal to noise ratios by limiting the spatial extent of the excitation or reception.
See also the related poll result: ' 3rd party coils are better than the original manufacturer coils' | |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'Surface Coil' (81).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | Basics:
|
|
| |
|  | |  |  |
|  | | |
|
| |
 | Look
Ups |
| |