(IR) The
inversion recovery pulse sequence produces signals, which represent the
longitudinal magnetization existing after the application of a 180°
radio frequency pulse that rotates the
magnetization Mz into the negative plane. After an
inversion time (TI - time between the starting 180° pulse and the following 90° pulse), a further 90°
RF pulse tilts some or all of the z-magnetization into the xy-plane, where the signal is usually rephased with a 180° pulse as in the
spin echo sequence. During the initial time period, various tissues relax with their intrinsic T1
relaxation time.
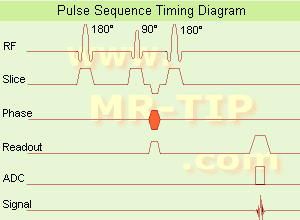
In the
pulse sequence timing diagram, the basic
inversion recovery sequence is illust
rated. The 180°
inversion pulse is attached prior to the 90°
excitation pulse of a
spin echo acquisition.
See also the
Pulse Sequence Timing Diagram. There you will find a description of the components.
The
inversion recovery sequence has the advantage, that it can provide very strong
contrast between tissues having different
T1 relaxation times or to suppress tissues like fluid or fat.
But the disadvantage is, that the additional
inversion radio frequency RF pulse makes this sequence less time efficient than the other pulse
sequences.
Contrast values:
PD weighted: TE: 10-20 ms, TR: 2000 ms, TI: 1800 ms
T1 weighted: TE: 10-20 ms, TR: 2000 ms, TI: 400-800 ms
T2 weighted: TE: 70 ms, TR: 2000 ms, TI: 400-800 ms
See also
Inversion Recovery,
Short T1 Inversion Recovery,
Fluid Attenuation Inversion Recovery, and
Acronyms for 'Inversion Recovery Sequence' from different manufacturers.