 | Info
Sheets |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
 | Out-
side |
| | | | |
|
| | | | | |  | Searchterm 'Device' was also found in the following services: | | | | |
|  |  |
| |
|
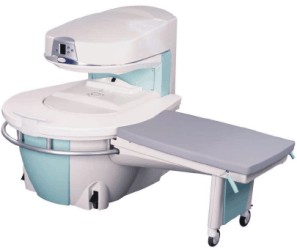
Manufactured by Esaote S.p.A.;
a low field open MRI scanner with permanent magnet for orthopedic use. The outstanding feature of this MRI system is a patient friendly design with 24 cm diameter, which allows the imaging of extremities and small body parts like shoulder MRI. The power consumption is around 1.3 kW and the needed minimum floor space is an area of 16 sq m.
At RSNA 2006 Hologic Inc. introduced a new dedicated extremity MRI scanner, the Opera. Manufactured by Esaote is the Opera a redesign of Esaote's 0.2 Tesla E-Scan XQ platform, which now enables complete imaging of all extremities, including hip and shoulder applications. 'Real-time positioning' reportedly speeds patient setup and reduces exam times.
Esaote North America and Hologic Inc are the U.S. distributors of this MRI device.
Device Information and Specification CLINICAL APPLICATION Dedicated extremity
SE, GE, IR, STIR, FSE, 3D CE, GE-STIR, 3D GE, ME, TME, HSE IMAGING MODES Single, multislice, volume study, fast scan, multi slab2D: 2 mm - 10 mm;
3D: 0.6 mm - 10 mm 4096 gray lvls, 256 lvls in 3D POWER REQUIREMENTS 2,0 kW; 110/220 V single phase | |  | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | News & More:
|
|
| |
|  |  | Searchterm 'Device' was also found in the following services: | | | | |
|  |  |
| |
|
(PACS) A system used to communicate and archive medical imaging data, mostly images and associated textural data generated in a radiology department, and disseminated throughout the hospital. A PACS is usually based on the DICOM ( Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine) standard.
The main components in the PACS are:
•
acquisition devices where the images are acquired,
•
short and longer term archives for storage of digital and textural data,
•
a database and database management,
•
diagnostic and review workstations,
•
software to run the system,
•
a communication network linking the system components,
•
interfaces with other networks (hospital and radiological information systems).
Acquisition devices, which acquire their data in direct digital format, like a MRI system, are most easily integrated into a PACS.
Short term archives need to have rapid access, such as provided by a RAID (redundant array of independent disks), whereas long term archives need not have such rapid access and can be consigned, e.g. to optical disks or a magnetic.
High speed networks are necessary for rapid transmission of imaging data from the short term archive to the diagnostic workstations. Optical fiber, ATM (asynchronous transfer mode), fast or switched Ethernet, are examples of high speed transmission networks, whereas demographic textural data may be transmitted along conventional Ethernet.
Sophisticated software is a major element in any hospital-wide PACS. The software concepts include: preloading or prefetching of historical images pertinent to current examinations, worklists and folders to subdivide the vast mass of data acquired in a PACS in a form, which is easy and practical to access, default display protocols whereby images are automatically displayed on workstation monitors in a prearranged clinically logical order and format, and protocols radiologists can rapidly report worklists of undictated examinations, using a minimum of computer manipulation. | |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'Picture Archiving and Communication System' (5).
| | |
• View the NEWS results for 'Picture Archiving and Communication System' (1).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | Basics:
|
|
| |
|  | |  |  |  |
| |
|
A device that amplifies very low-level signals. A preamplifier is generally placed close to its signal source and has a very low noise figure as it is the principal determinant of electronic noise within the system. Preamplifiers used in NMR systems usually have a 50 ohm input impedance, and require a matching network to interface to the RF coil, although preamplifiers with high input impedance may be used with surface coils. Such devices typically use a field effect transistor (FET) as their input stage. | |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'Preamplifier' (5).
| | | | |
|  |  | Searchterm 'Device' was also found in the following services: | | | | |
|  |  |
| |
|
Quick Overview Please note that there are different common names for this artifact.
DESCRIPTION
Static on the image
REASON
Electromagnetic emissions
HELP
Shielding, eliminate the factor of disturbance
RF noise, which often appears as static on the image, can be caused by a medical device located anywhere in the MR procedure room.
RF noise is a result of excessive electromagnetic emissions from the device that interference with the proper operation of the MR scanner.
The interference is attenuated and aliased in the frequency direction.

Image Guidance
| |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'Radio Frequency Noise Artifact' (3).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | Basics:
|
|
| |
|  |  | Searchterm 'Device' was also found in the following services: | | | | |
|  |  |
| |
|
(RIS) Radiology information system means a computer system that stores and processes the information for a radiology department and can be linked to the hospital information system.
The principal purpose of a RIS consists of taking over the general functions of the administration inclusive planning, monitoring and communication of all data regarding patients and its investigations in the radiology. The correct images should reach, at the correct time, the correct users. For this reason the RIS must contain a workflow management in order to simplify and steer the data flow at the individual view stations or devices (laser cameras etc.). The Radiology Information System is optimally complemented with a Picture Archiving and Communication System (PACS).
•
Collection, storage and administration of patient master data
•
Archives administration
Treatment of requirements
•
Communication (with the hospital information system, MRI scanner, other devices etc.)
| |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'Radiology Information System' (3).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | Basics:
|
|
| |
|  | |  |  |
|  | |
|  | | |
|
| |
 | Look
Ups |
| |