 | Info
Sheets |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
 | Out-
side |
| | | | |
|
| | | | | |  | Searchterm 'Spectroscopy' was also found in the following services: | | | | |
|  |  |
| |
|
(ISIS) Image selected in vivo spectroscopy is used as a localization sequence to provide complete gradient controlled three-dimensional localization with a reduced number of sequence cycles, e.g. for in vivo 31P spectroscopy.
The ISIS method generates three 180┬░ pulses prior to a 90┬░ pulse, after which the free induction decay is recorded. Specific 180┬░ pulses (slice-selective) are combined and the FID's added or subtracted to generate a spectrum.
An advantage of the ISIS method is that the magnetization (before the final 90┬░ pulse) is predominantly along the z-axis and so T2 effects are relatively small. This explains the value of this technique for 31P data acquisition, because some phosphorus metabolites (e.g. ATP) have short T2 values.
A disadvantage is that eight acquisitions are required to accomplish the spatial localization, therefore the sequence cannot be used for localized shimming.
Another problem, because any variation between these data collections (for example, due to movement) will degrade these applications, can be solved by incorporating outer volume suppression techniques such as OSIRIS (modified ISIS). | |  | | | |
|  |  | Searchterm 'Spectroscopy' was also found in the following service: | | | | |
|  | |  | |  |  |  |
| |
|
For the wide uses of NMR spectroscopy (from mineralogy to medicine) there is a variety of different spectroscopic imaging techniques available.
A short listing of the most frequent variations:
•
'Two-dimensional NMR Spectroscopy' (2D NMR) is based on pulse spectroscopy. This technique is mostly used for the study of chemical interactions accompanied by magnetization transfer. Examples for more diversified spectroscopy techniques are based on homonuclear (COSY, TOCSY, 2D-INADEQUATE, NOESY, ROESY) or heteronuclear correlation (HSQC, HMQC, HMBC).
•
'Solid State NMR Spectroscopy' analyzes samples with little or no molecular mobility. Dipolar coupling and chemical shift anisotropy are the dominating nuclear physical effects here. Used for example in pharmaceutical analysis.
•
'Solution State NMR Spectroscopy' is a technique to analyze the structure of samples with a high degree of molecular mobility as polymers, proteins, nucleic acids etc.
| |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'Spectroscopic Imaging Techniques' (2).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | | Basics:
|
|
News & More:
| |
| |
|  |  | Searchterm 'Spectroscopy' was also found in the following services: | | | | |
|  |  |
| |
|

Swiss-based, formerly Bruker AG - split on the 5th October 2001 into the groups: Bruker Daltonics ( Mass spectroscopy), Bruker Optics (Infrared spectroscopy), Bruker AXS (X-ray spectroscopy) and Bruker BioSpin (The largest part, the NMR business core, the EPR and the Tomography activities).
Product Lines:
•
PharmaScan® - MRI//MRS systems tailored to high-throughput and routine applications in pharmaceutical research.
Product Specification
Contact Information
Please see Bruker BioSpin AG's
| |  | |
• View the NEWS results for 'Bruker BioSpin AG' (1).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | News & More:
|
|
| |
|  |  | Searchterm 'Spectroscopy' was also found in the following service: | | | | |
|  |  |
| |
|
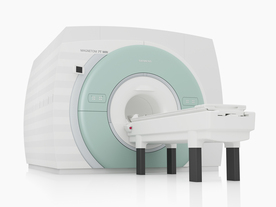
From Siemens Medical Systems;
The MAGNETOM 7T is designed as an open research platform. 7T MRI provides anatomical detail at the submillimiter scale, enhanced contrast mechanisms, outstanding spectroscopy performance, ultra-high resolution functional imaging ( fMRI), multinuclear whole-body MRI and functional information.
This ultra high field (UHF) MRI device is a research system and not cleared, approved or licensed in any jurisdiction for patient examinations.
Device Information and Specification
CLINICAL APPLICATION
Whole body
High-performance, ultra high field coils available. Integration and support for coil developments.
CHANNELS (min. / max. configuration)
32, optional 8 channels TX array
40 x 40 x 30 cm³ less than 8% nonlinearity
MAGNET WEIGHT (gantry included)
35017 kg
DIMENSION H*W*D (gantry included)
320 x 240 x 317,5 cm
MAX. AMPLITUDE
up to 70 mT/m
Up to 3rd order shim coils, user configurable B0 shim ? B0 maps and ROI definition
POWER REQUIREMENTS
2000 Volts, 650A
| |  | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | Basics:
|
|
News & More:
| |
| |
|  | |  |  |
|  | | |
|
| |
 | Look
Ups |
| |