|
Magnetic
Resonance -
Technology
Information
Portal |
Welcome to MRI Technology • • |
|
|
 | Info
Sheets |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
 | Out-
side |
| | | | |
|
| | | | |
Result : Searchterm 'Hardware' found in 1 term [ ] and 20 definitions [ ] and 20 definitions [ ] ]
| previous 6 - 10 (of 21) nextResult Pages :  [1] [1]  [2 3 4 5] [2 3 4 5] |  | |  | Searchterm 'Hardware' was also found in the following services: | | | | |
|  |  |
| |
|
Quick Overview
DESCRIPTION
Incorrectly interpretation or display
HELP
Save to a new or different media
An artifact on a MR image can appear when data read off an optical disc became corrupted. There two effects can be seen.
Firstly, Bands where the intensity has been incorrectly interpreted or secondly areas, where the horizontal position of the pixels has been incorrectly displayed. It is important to be able to differentiate between artifacts caused during a MRI scan, from those caused by the associated hardware of an imaging system.

Image Guidance
Review the hardware and store the images on a new disc. | |  | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | Basics:
|
|
| |
|  |  | Searchterm 'Hardware' was also found in the following services: | | | | |
|  |  |
| |
|
Quick Overview
This artifact is uncommon with modern MRI equipment, but possible. It can occur if there are bad memory locations or bad connectors in the parallel data bus of the computer.

Image Guidance
This artifact is the result of a hardware failure and must be addressed by a service representative. | |  | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | News & More:
|
|
| |
|  | |  |  |  |
| |
|
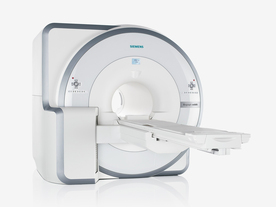
FDA cleared and CE Mark 2011.
The Biograph mMR has a fully-integrated design for simultaneous PET/MRI imaging. The dedicated hardware includes solid-state, avalanche photodiode PET detector and adapted, PET-compatible MR coils.
The possibility of truly simultaneous operation allows the acquisition of several magnetic resonance imaging ( MRI) sequences during the positron emission tomography (PET) scan, without increasing the examination time.
See also Hybrid Imaging.
Device Information and Specification
CLINICAL APPLICATION
Whole Body
CONFIGURATION
Simultaneous PET/MRI
26 cm (typical overlap 23%)
A-P 45, R-L 50, H-F 50 cm
PET RING DIAMETER
65.6 cm
PATIENT SCAN RANGE
199 cm
HORIZONTAL SPEED
200 mmsec
PET DETECTOR
Solid state, 4032 avalanche photo diodes
DETECTOR SCINTILLATION MATERIAL
LSO, 28672 crystals
CRYSTAL SIZE
4 x 4 x 20 mm
DIMENSION H*W*D (gantry included)
335 x 230 x 242 cm (finshed covers)
COOLING SYSTEM
PET system: water; MRI system: water
Aautomatic, patient specific shim; active shim 3 linear and 5 non-linear channels (seond order)
POWER REQUIREMENTS
380 / 400 / 420 / 440 / 460 / 480 V, 3-phase + ground; Total system 110kW
| |  | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | | Basics:
|
|
News & More:
| |
| |
|  |  | Searchterm 'Hardware' was also found in the following services: | | | | |
|  | |  |  | Searchterm 'Hardware' was also found in the following services: | | | | |
|  |  |
| |
|
Quick Overview Please note that there are different common names for this artifact.
This artifact appears as a bright spot (or zipper line) in the image center. Central point artifacts are caused by a DC offset in the hardware. MRI scanners normally offer a software compensation (DC correction, baseline correction) for prevention.

Image Guidance
Take care for a constant temperature. If the problem increases or keeps on existing, it should be addressed to the service. | |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'Central Point Artifact' (4).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | | Basics:
|
|
News & More:
| |
| |
|  | |  |  |
|  | | |
|
| |
 | Look
Ups |
| |
|
MR-TIP.com uses cookies! By browsing MR-TIP.com, you agree to our use of cookies. | | | [last update: 2024-02-26 03:41:00] |
|
|